All about Primary Batteries
Essential to our daily lives, batteries come in a variety of sizes, shapes, compositions and technologies, each with its own specific features. Discover how they work, their differences and the importance of recycling them.
What is a battery?
A battery, or disposable battery, is a small, portable generator that converts the energy of a chemical reaction into electricity. Unlike batteries (or accumulators), they are disposable and non-rechargeable.
How do batteries work?
A battery consists of two electrodes, a cathode (positive pole) and an anode (negative pole), immersed in a conductive solution.
When a conductive wire connects these electrodes to an electrical device, such as a light bulb, the circuit is closed. A current of electrons flows from one pole of the battery to the other, through the conductive solution. This generates electricity.
This electricity-generating process relies on the energy released by a chemical reaction. Once this reaction is complete, the battery is discharged and must be replaced.
What is a battery made of?

A stack is generally composed of the same elements, namely :
- Plastic.
- Paper (battery packaging).
- Various metals: zinc, iron, nickel, manganese...
Depending on the type of battery, the materials and other compounds are different.
What are the different types of batteries?

There are several types of battery, each based on a specific technology that influences both composition and use.
Salt batteries
Most contain zinc, carbon or manganese and an acid electrolyte (ammonium chloride, for example).
- Inexpensive.
- Use: energy-efficient devices (clocks, radios, remote controls, construction site lights, etc.).
Alkaline batteries
Made from steel, zinc, manganese and a basic electrolyte (mainly soda or potash).
- Low price (but more expensive than salt batteries).
- Use: low- to high-energy consumption devices (all-purpose). High-performance, they discharge less quickly if left unused for long periods.
Zinc-air batteries
Mainly made of zinc.
- Application: Characterized by their "button" shape (hearing aids, electric fences for livestock, in the most voluminous forms).
Organic lithium batteries
Made of steel, lithium and manganese (most often).
- Relatively expensive.
- Use: Lightweight, last 5 times longer than alkaline batteries.
- Good to know! For an equivalent voltage, lithium batteries are used half as much. More powerful, they deliver 3.5 V (vs. 1.5 V for alkaline batteries), reducing weight and bulk.
Inorganic lithium batteries
These contain steel, sulfur dioxide or thionyl chloride, lithium and a highly flammable organic electrolyte.
- Very high price, so not widely available for retail sale.
- Use: For military or highly technical applications.
Zinc-silver batteries
Made of steel, zinc and silver.
- Available mainly in "button" form.
- Use: small objects (watches, clocks, hearing aids, toys, electronic gadgets, etc.).
Mercury batteries
Contain steel, zinc and mercury.
- Available for sale in "button" form, for very specific and limited uses.
- Use: Old watches or clocks
What is a button cell?
The term "button cell" refers to a type of battery, not a technology. Used in small devices, they can be based on :
- Mercury (up to 25%, regulated use).
- Zinc-silver.
- Alkaline.
- Lithium-manganese (or organic lithium).
Did you know that ?
-
104
Is the average number of batteries hidden in French households
-
of which 14 %
Are used and awaiting recycling
Why recycle batteries?
Disposed of in household waste or in the environment, batteries are harmful to health and the environment. Lead, zinc, nickel, cadmium, mercury and other metals can end up in our soil, polluting it for a long time to come.
Every used battery returned to a collection point counts!
- Almost 80% of the materials used to make them can be recycled.
- Metals and alloys derived from recycling will be reused to make new objects.
- The extraction of raw materials will be reduced, thus lessening the impact on nature.
- The second life of batteries, made possible by recycling, limits our energy dependence on metal-supplying countries.
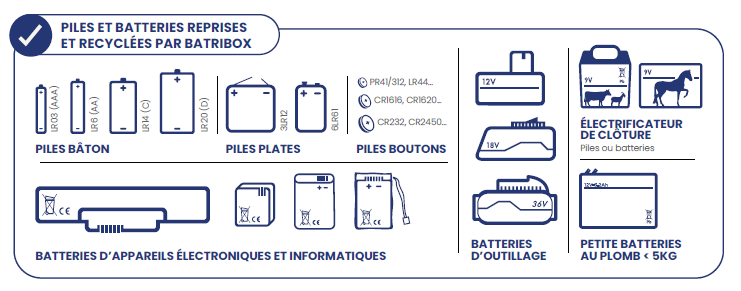
Where to dispose of used batteries?
Alkaline, saline, lithium, zinc-air, zinc-silver and other button cells are collected and recycled by Batribox.
Found in many everyday objects, you can return your used batteries to one of our 32,222 collection points: stores, offices, waste collection centers, schools, town halls...
Once collected, batteries are sorted by technology: alkaline-saline, lithium, button cell. They are then directed to the appropriate recycling channels.
Find your nearest collection point!
Research scope
Search result
Adopt the recycling reflex!
Whether at home or at school, every gesture counts in preserving our resources. Find out how Batribox supports private individuals and schools in collecting and raising awareness.